Five-Step Female Hair Loss Treatment
Even though hair loss is viewed as a problem that mostly occurs in the lives of men, women are almost as likely to suffer from thinning hair. It could be an issue for women of any age but is more common in middle age women and women that are experiencing menopause. Female hair loss can happen for a variety of reasons as will be discussed below.
While typical male patterned hair loss occurs on the corners or baldness on the crown, women usually have more diffuse thinning (spread out over a large area) on both the front and top of the scalp. Hair loss can be a big blow to the image and self-esteem of women. Not every case of female hair loss is a perfect fit for a hair transplant. However, some female hair loss patients can benefit from a hair transplant. Thanks to evaluating thousands of women who suffered from female hair loss in our Los Angeles hair restoration office, we have the experience and knowledge to formulate a step by step approach for this common condition.
Here are five steps any hair specialist may need to take to diagnose and manage female hair loss as well as prevent any future loss.
Step 1: History
The first, and maybe most important, step in managing female hair loss is taking an accurate patient history. This history should include:
- Family history of hair loss and more specifically a trend of female hair loss
- History of any current or past medical problems
- Surgical history
- Medications for hair loss and other conditions
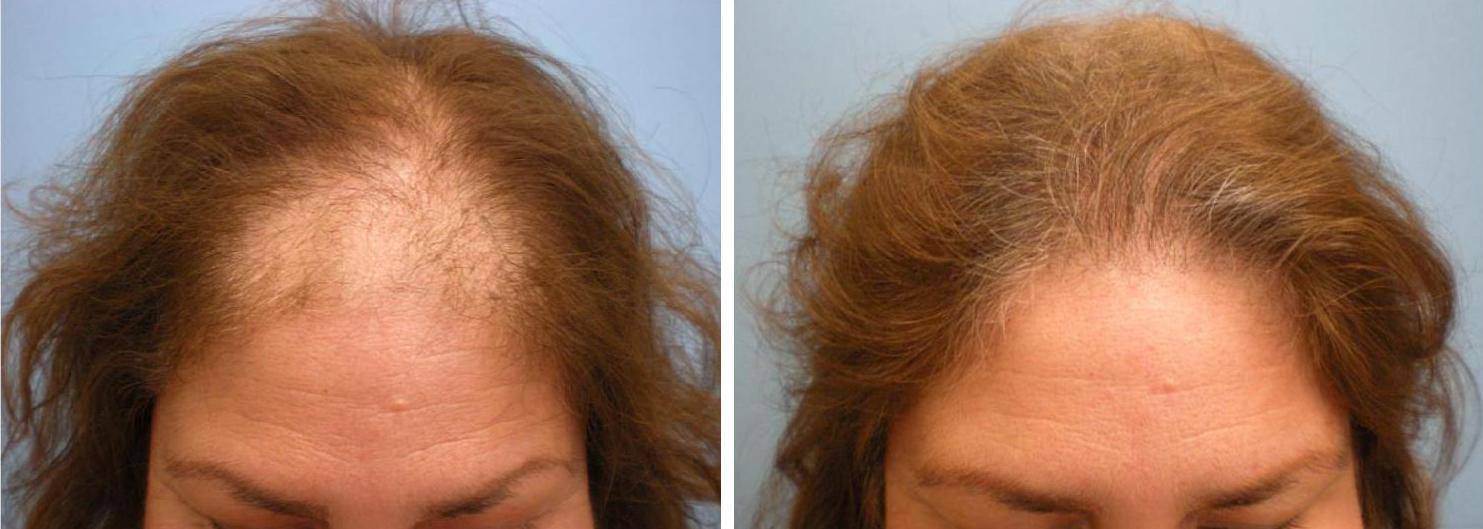
We usually see a strong family history of hair loss in both male and female patterned hair loss. If there is no family history of female hair loss, we need to start looking for other causes of hair loss. Many medical conditions can cause hair loss or accelerated hair loss in people who are prone to it. Some procedures, and specifically scalp surgeries, can lead to scarring or other types of hair loss so it is important to inquire about those as well. There are some medications that have hair loss as one of their known side effects. A complete medical history is vital in the evaluation and diagnosis of the cause of the hair loss experienced by the patient.
Step 2: Macro and Microscopic Evaluation of Scalp and Hair
A thorough examination of the patient’s scalp should be performed to determine if there are any abnormal patterns present. Observation of the scalp in different areas is sufficient to diagnose some types of hair loss such as congenital hair loss, hair loss due to scarring and most patterned hair loss. Microscopic evaluation of the scalp, as well as the hair, is a big component in evaluating hair loss in a female patient. In patterned hair loss, hair shafts always become fine before they are lost. This phenomenon, also called miniaturization, is ideal to differentiate patterned hair loss from other hair loss causes such as autoimmune hair loss conditions in which we can see a lack of hair without the presence of miniaturization. If the patient has more than twenty percent miniaturization in any areas of the scalp, that usually indicates active hair loss in that area. The mapping of scalp hair miniaturization is also a helpful guide to evaluate the effectiveness of medical treatment.
Step 3: Hair Loss Lab Work
Lab work is not always needed in the workup of hair loss conditions. However, it might be necessary for some types of female hair loss conditions. The lab work can range from a CBC (Complete Blood Count) to an Iron Panel and hormonal levels. The Iron Panel may include serum iron levels, TIBC (Total Iron Binding Capacity) and ferritin levels (measure the amount of iron stored in the body).
Hormonal levels will also need to be checked in the patient because hormonal imbalances can be a reason for hair loss and thinning in women. The most common levels checked in hair loss workup include:
- Total and Free Testosterone
- DEHA-Sulfate
- Prolactin
- T3, T4 and TSH
After these tests are completed, there might be a need for a few other specific tests. Also, the doctor may have to obtain a scalp biopsy in order to eliminate the possibility of other skin conditions leading to the hair loss. Examples of these conditions include Alopecia Areata and Alopecia Cicatricial. The need for a scalp biopsy is evaluated on an individual patient basis.
Step 4: Hair Loss Diagnosis
The decision of what treatment to undertake for the patient’s hair loss is decided after a diagnosis from the doctor. If there is a medical condition causing the hair loss, it must be addressed before any treatment plan is undertaken. If we don’t discover another medical condition causing the hair loss, the most likely diagnosis is male or female patterned baldness. We may offer a variety of treatments for each condition.
Step 5: Hair Loss Treatment
One of the common types of hair loss conditions in women is diffuse hair loss. Patients experience a high level of thinning hair and we can also detect high rates of miniaturization of hair in our microscopic examination of the person. Patients who have a high level of miniaturization are generally not good candidates for a hair transplant. These patients mostly require medical hair loss treatment with minoxidil (Rogaine) and low level laser therapy (LLLT).
Who is a good candidate for a Female Hair Transplant?
- The best candidates are women with male patterned balding that have non-defuse loss of hair with preserved donor hair on the permanent zone.
- Women who have a congenitally high hairline and want to reduce the height of their forehead and create a more feminine hairline.
One important aspect of hair loss treatment is making sure expectations are set at an attainable level. Not all patients can expect to see the same outcome and should enter the treatment process with a realistic goal in mind. Also, more than one transplant may be required for the best results in some women. The patient should be aware of this fact in advance.
Five Easy Steps to Female Hair Loss Management
| Diagnosis | MPB | FPB | Other Medical Conditions |
| Hair Loss Type | Local not diffuse | Diffuse | Varies |
| Medical Treatment | Anti-androgen if hyperandrogenism | Rogaine and Laser Treatment | Observe and treat underlying cause |
| Hair Transplant | Always good candidate | Usually not indicated | Usually not indicated |
Table 1: Association of each diagnosis of female patterned hair loss with its treatment options.
A specialist in the field of female hair loss should have a good working knowledge of cosmetics which are useful in enhancing the appearance of women suffering from male or female patterned hair loss. The specialist should be knowledgeable about various shampoos, conditioners and other hair products and their effects (good and bad) on hair appearance. Learning how to properly style your hair to avoid further damage, hair coloring tips and other cosmetic changes to a daily hairstyle routine can be a big help in the hair loss consultation process.
Female Hair Loss Treatment
The approach used to treat women who suffer from hair loss is different than the treatment of men who suffer from typical male patterned baldness. A thorough evaluation and correct diagnosis can make all the difference in the success of the treatment. In some cases, deciding on medical treatments to maintain the current scalp hair might be a better option than a hair transplant. No matter what option is chosen, it is vital to make sure all parties enter the treatment with the same expectations. The challenges of dealing with, and correcting, extensive hair loss can lead to a life changing experience for patients. A well planned combination of medical treatments, hair transplantation and cosmetic choices can work wonders in creating the optimum appearance of full and healthy hair in women who suffer from hair loss.